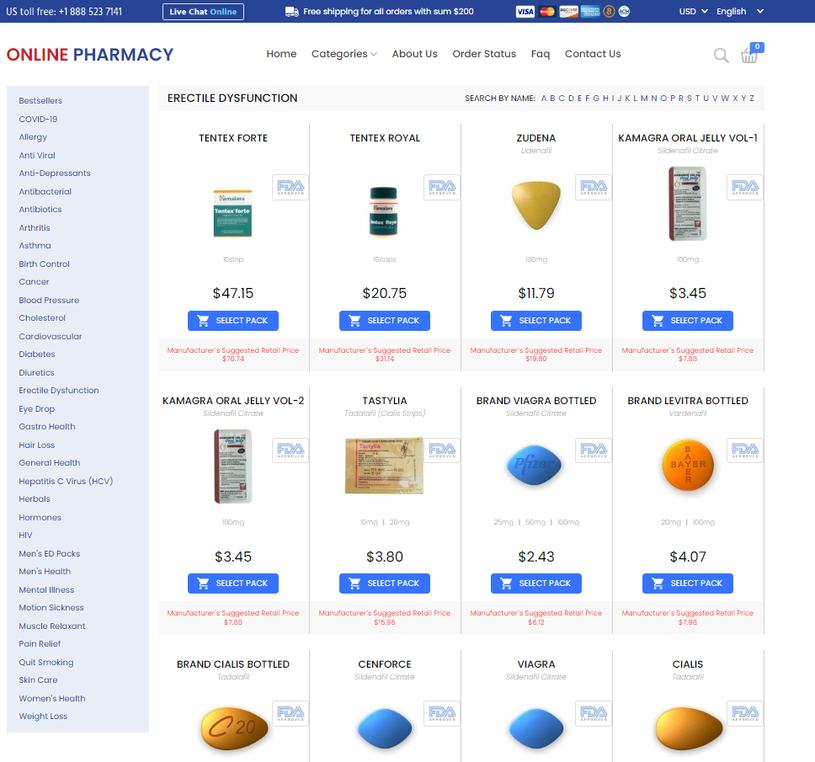
To Purchase Bactrim Without Prescription Visit Our Pharmacy ↓
Potential Side Effects: Debunking the Fear Factor
In addition to UTIs and respiratory infections, Bactrim is also used to treat other types of bacterial infections, such as skin and soft tissue infections. The strategic combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole targets the bacteria's capacity to produce essential proteins and nucleic acids, thereby thwarting the infection's proliferation and aiding in the rapid restoration of urinary tract health. This synergistic duo blocks two consecutive steps in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins essential for many bacteria. UTIs are a common ailment, especially among women, and Bactrim has proven to be highly effective in treating these infections. Bactrim, a commonly prescribed antibiotic, is widely known for its effectiveness in treating various bacterial infections. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate alternative treatment option based on the specific infection and individual circumstances. Bactrim can be prescribed for bacterial sinusitis, bronchitis, and pneumonia.
Rare but Serious Reactions: When to Seek Help
This can manifest as a rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing. Additionally, incorporating antifungal medications can be beneficial for fungal skin infections that may not respond adequately to Bactrim alone. Sulfamethoxazole disrupts the production of folic acid, an essential nutrient for bacterial cell growth, while trimethoprim inhibits the enzyme involved in folic acid synthesis. However, it is important to note that Bactrim is only effective against bacterial infections and does not work against viral infections like the common cold or flu. Its broad-spectrum antibiotic properties make it a reliable option for conditions such as urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, and skin infections. Bactrim's remarkable antibacterial efficacy has positioned it as a potential game-changer in the field of medicine. This blockade is highly effective against a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, making Bactrim a potent choice for treating UTIs.
Common Myths Surrounding Bactrim: Setting the Record Straight
In the case of difficulty breathing or any other severe reaction, call emergency services without delay. Moreover, it is worth mentioning that the benefits of using Bactrim to treat bacterial infections often outweigh the potential risks. This condition, characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, can be managed with the help of Bactrim's antimicrobial properties. Clinically, this translates to a higher likelihood of successfully treating uncomplicated UTIs, accelerating patient recovery, and reducing the likelihood of recurrent infections when used appropriately. Certain medications, such as blood thinners, diuretics, or medications that affect the liver or kidneys, may interact with Bactrim and lead to adverse effects. This combination antibiotic, consisting of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, is equipped with battle-ready chemistry that targets and eliminates the underlying causes of respiratory infections. Additionally, some may notice skin rashes, a light sensitivity, or even mild headache; these reactions can be bothersome but are typically manageable.
Possible Pitfalls: Recognizing Bactrim's Side Effects
UTIs can be incredibly disruptive, causing pain, discomfort, and a decreased quality of life. To understand how Bactrim works, it is important to delve into its mechanism of action. This interaction underscores the need for healthcare providers to review and adjust dosage regimens or seek alternative treatments to avoid adverse effects. From bacterial bronchitis to pneumonia, Bactrim has proven its resilience in the face of these infections, providing relief to countless individuals. Due to its potent action and broad-spectrum coverage, Bactrim has proven to be an essential tool in the fight against bacterial infections. Another misconception is that Bactrim can cause immediate symptom relief. Common side effects of Bactrim may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of appetite.
Comparing Costs: Bactrim Vs
In one revealing case, a young woman prescribed Bactrim for a severe UTIs felt well enough to attend a party. Nausea and vomiting are frequently reported, often leading to discomfort and an aversion to eating. Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern in today's world, but Bactrim remains an effective treatment option. Without adequate tetrahydrofolic acid, bacteria are unable to properly function and replicate, leading to their eventual death or elimination. Bactrim, an antibiotic medication, owes its effectiveness to the synergistic actions of two active ingredients: sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Like any medication, Bactrim comes with a spectrum of potential side effects that patients should be aware of. Understanding these potential side effects can help you prepare and minimize their impact on daily life.
Potential Side Effects and Precautions.
Despite its efficacy, it can elicit reactions that are frequently misattributed to other causes. Bactrim is known for its effectiveness in treating various bacterial infections. However, it is crucial to follow the prescribed treatment duration to ensure the complete eradication of the bacteria and prevent the development of antibiotic resistance. Trimethoprim, on the other hand, is a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor. Studies have shown that Bactrim, when combined with other antibiotics, can effectively combat pneumonia caused by certain bacteria. This includes developing novel drug delivery methods such as nanoparticles or liposomes, which can improve drug stability, control release, and target specific bacterial strains or infection sites. By inhibiting these enzymes, Bactrim disrupts the production of folic acid in bacteria, leading to their eventual death.
Common Uses: Treating Urinary Tract Infections, Respiratory Infections, and More
A conscientious approach to reading labels and consulting with a pharmacist can be crucial in avoiding unintended alcohol intake. Nonetheless, its use is tempered by emerging resistance concerns. By taking a low dose of Bactrim over an extended period of time, individuals prone to recurring UTIs may be able to reduce the frequency and severity of their infections. Antibiotic resistance is a growing concern globally, with the overuse and misuse of antibiotics playing a significant role in the emergence of resistant bacteria. However, like any medication, it may cause side effects in some individuals. Bactrim is commonly used to treat a variety of skin infections, ranging from simple impetigo to more complex cellulitis and abscesses. Some patients may also experience a rash or itching, which, if accompanied by fever or blisters, should prompt immediate medical attention.
Common Antibiotics: a Comparative Snapshot
Trimethoprim selectively targets and inhibits this enzyme in bacteria, leading to a reduction in tetrahydrofolic acid levels. While Bactrim's powerful antimicrobial properties are well-known, its favorable safety profile is equally noteworthy. Some patients may experience allergic reactions, such as hives or anaphylaxis, particularly if they have a known allergy to sulfa drugs. By taking the medication as directed by a healthcare professional, patients can experience relief from the painful symptoms of UTIs and achieve a full recovery. Certain individuals need to approach Bactrim with caution due to potential health implications. Thus, exploring alternative treatment options can provide suitable alternatives to Bactrim in certain cases. John’s Wort may decrease the effectiveness of the antibiotic, leading to reduced ability to combat infections.
Dietary Dangers: Foods and Supplements to Avoid
Healthcare providers must thoroughly review patients' medication regimens and remain vigilant for signs of adverse effects, which are often subtle and insidious in onset. The combination of trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole that constitutes Bactrim targets multiple bacterial pathways, enhancing its ability to obliterate diverse bacterial species. Accounts of nausea, severe headaches, and hypersensitivity reactions surface in discussions, emphasizing the importance of monitoring individual responses to Bactrim. Bactrim, also known as a prescription antibiotic, is commonly used to treat a variety of skin infections. To minimize the risks associated with consuming alcohol while taking Bactrim, it's crucial to adhere to the advice of healthcare professionals. Trimethoprim, a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor, further inhibits the production of folic acid by blocking the enzyme responsible for its synthesis. However, there is a ray of hope in the form of Bactrim, a powerful antibiotic that continues to exhibit effectiveness in combating UTIs despite the rising resistance trends.
Common Side Effects: What to Expect While Taking
When it comes to treating skin issues, Bactrim demonstrates its potency by targeting the underlying bacterial culprits responsible for the infection. As a consequence, he developed a pronounced skin rash and heightened jaundice due to the antibiotic's inhibited efficacy and the strain on his liver, complicating his infection management and requiring additional medical intervention to remedy the damage caused by this dangerous cocktail. However, its uses extend beyond just infections. Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal issues such as nausea or diarrhea, while others may develop allergic reactions like rashes or itching. Mixing Bactrim and alcohol can amplify side effects, creating a more unpleasant experience for patients. Its distinct advantage lies in the dual-action mechanism that disrupts bacterial folate synthesis, offering a broader spectrum of action compared to some single-agent antibiotics. The wide spectrum of effectiveness of Bactrim makes it a versatile choice for clinicians, allowing for a more streamlined approach to treatment.